Enterprise JavaBeans™ EJB 3.0
UML Profile Diagram Example
Here we provide an example of simplified and unofficial UML Profile for Enterprise JavaBeans™ (EJB) 3.0 with support for session, entity, and message-driven Enterprise JavaBeans.
Official Metamodel and UML Profile for Java and EJB Specification, Version 1.0 by OMG and JCP [UML Profile for Java and EJB. Version 1.0] is for Java 1.3, EJB 1.1 and most likely UML 1.4, so it could be only of some interest to bookworms.
UML 2.4 specification [UML 2.4 - Superstructure] provides example profile for unspecified version of J2EE/Enterprise Java Beans (EJB) in Annex D.1. That UML sample profile is neither normative (official) nor complete, and is provided only as an illustration.
The EJB 3.0 specification defines both stateful and stateless session beans. There are differences in the API between stateful session beans and stateless session beans. The client of a session bean may be a local client, a remote client, or a web service client, depending on the interface provided by the bean and used by the client.
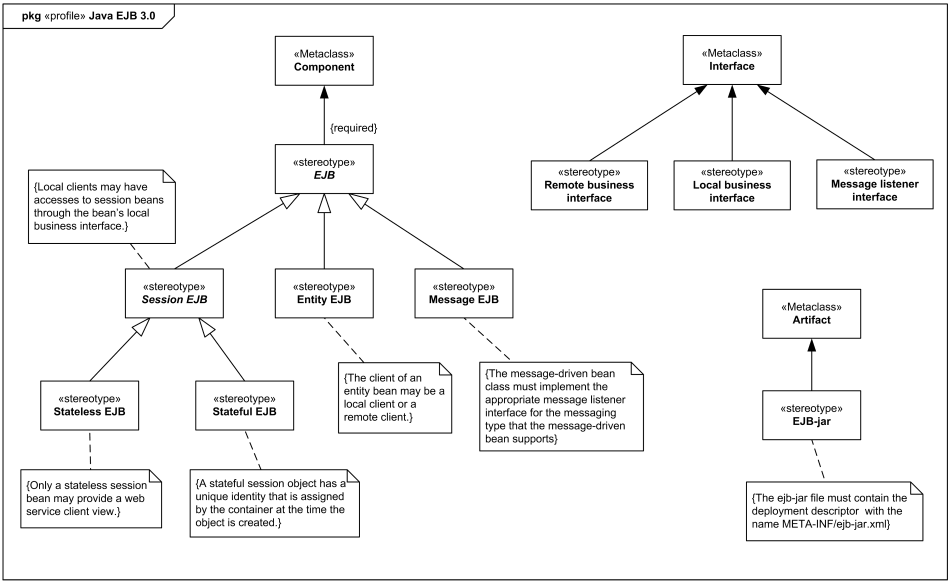
Simplified example of unofficial Java EJB 3.0 Profile
Stateful session bean represents a conversational session with a particular client. Such session objects automatically maintain their conversational state across multiple client-invoked methods.
An entity object represents a fine-grained persistent object. The client of an entity bean may be a local client or the client may be a remote client.
The message-driven bean class must implement the appropriate message listener interface for the messaging type that the message-driven bean supports or specify the message listener interface using the MessageDriven metadata annotation or the messaging-type deployment descriptor element.
The ejb-jar file must contain the deployment descriptor in the format defined in EJB Specification. The deployment descriptor must be stored with the name META-INF/ejb-jar.xml